In the behaviorist learning theory, the idea is to create specific behaviors through rewards for wanted behaviors and consequences for unwanted behaviors. When it is applied to a classroom setting, it becomes a method of operant conditioning. It is used to not to help children understand the benefits of following the rules through a logical debate, but through the use of positive and negative reinforcement.
- Types Of Negative Reinforcement In The Classroom
- Is A Talking To Considered Negative Reinforcement
- Examples Of Positive And Negative Reinforcement
With the behaviorist learning theory in the classroom, there are four basic types of reinforcement that can be used.
Negative reinforcement. Negative reinforcement is just one more option available to educators who choose behavior modification as the basis for classroom management. Examples of Negative Reinforcement In order to gain practice with negative reinforcement, the reader should examine the following statements. Examples of Negative Reinforcement Quick Reminder of What Negative Reinforcement Is. Negative reinforcement occurs when something already present is removed (taken away) as a result of a behaviour and the behaviour that led to this removal will increase in the future because it created a favourable outcome. Reinforcement is a consequence following a behavior that increases the probability that the behavior will increase in the future. In addition to keeping behavior under control, reinforcement in the classroom should be used to keep students engaged and motivated to learn.
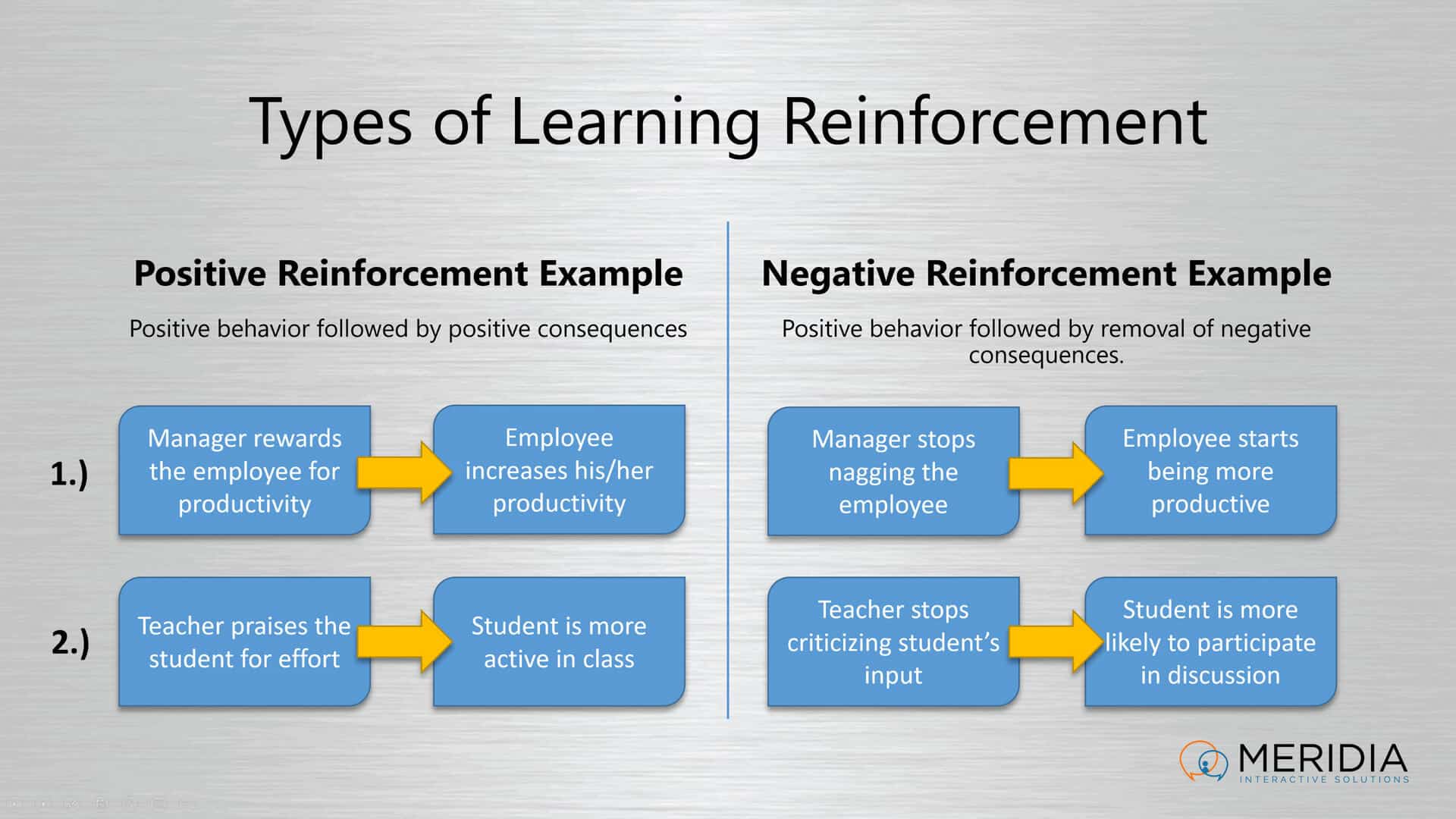
- Positive Reinforcement. This is an immediate reinforcement of a wanted behavior when it is observed. Giving a student verbal praise for a wanted behavior is a common form of positive reinforcement that teachers offer to students.
- Negative Reinforcement. Instead of offering a student a compliment, this type of reinforcement tells a student that their behavior is not wanted. The goal isn’t to embarrass the student, but to offer an alternative behavior that could bring about a desired reward.
- Presentation Punishment. This option is often used as a form of showing an entire class what will create a negative reinforcement response. If Johnny keeps yelling during story time, a teacher might bring the student up to the front of the class and then tell Johnny that his behavior is inappropriate at that moment. The goal here is to embarrass the student, but to also encourage other students not to be embarrassed by not replicating Johnny’s behavior.
- Removal Reinforcement. This may be used by removing a disruptive student with negative behaviors from the classroom. It may also be used through a period of negotiation so that a teacher gets what they want, but a student can also have something that they want.
The opposite of both of these concepts are social negative reinforcement and automatic negative reinforcement. The goal of social negative reinforcement is to get the child away from something or have something be taken away through the actions of someone else. So for example, a child might ask for their mother to take the fruit off their plate.
Each reinforcement opportunity has specific benefits and disadvantages that must be considered before it is implemented in a classroom setting.
Pros and Cons of Positive Reinforcement
Pros
It offers an immediate reinforcement of a wanted behavior. Specific statements of praise help to reinforce the compliment being offered. Specific actions, such as “clipping up” or “earning a star,” can also be included to initiate rewards.
Cons
Some students aren’t motivated by rewards. They don’t care about the classroom setting and will not respond to the positive reinforcement opportunities.
Pros and Cons of Negative Reinforcement
Pros
It creates an immediate “consequence” for an unwanted behavior. Some students may hear this consequence and not want to have it themselves, which will modify their behavior. It can create immediate change within a student who is motivated by rewards.
Cons
Some students are not motivated by a negative reinforcement either. “Who cares what you think?” Their behaviors are more about their individual needs and those needs don’t involve the classroom setting.
Pros and Cons of Presentation Punishment
Pros
It impacts the entire classroom. You’re able to modify the behavior of a large group by using an unwanted behavior from one individual. It can address a specific and potentially dangerous unwanted behavior immediately.
Cons
It causes the student being used as a presentation to be targeted by other students. They may make fun of that student or not want to be associated with them. Some students are sensitive and may resent being used as an example toward other students, which increases the number and the aggressiveness of their unwanted individuals.
Pros and Cons of Removal Reinforcement
Pros
It is a way to meet the needs of a specific student without disrupting the entire class. It may remove an unwanted behavior from the classroom immediately. Removal minimizes impact while allowing learning progression. It takes away something that a student sees as “good,” which encourages them to “earn it back” with wanted behaviors.
Cons
It may encourage a student to continue offering unwanted behaviors so they can get their way. They learn that there is a direct connection between behaving “badly” and getting what they want. It may cause other students in the classroom setting to behave in the same way so they can receive “special treatment” as well.
Which Option Is Right for Teachers Today?
Teachers should be using all of these options when appropriate to address wanted and unwanted behaviors in the classroom. The goal should always be to avoid an unpleasant consequence, but sometimes a punishment is necessary to remove an unwanted behavior. Teachers should never belittle a student. They should always be looking for a way to generate a positive outcome.
And behaviorist learning theory in the classroom works best when an individualized approach is taken. A group consequence creates resentment in students who weren’t involved. Group rewards only reinforce unwanted behaviors in those who weren’t meeting expectations. By finding the middle ground, the classroom can really become a good learning environment.
In the behaviorist learning theory, the idea is to create specific behaviors through rewards for wanted behaviors and consequences for unwanted behaviors. When it is applied to a classroom setting, it becomes a method of operant conditioning. It is used to not to help children understand the benefits of following the rules through a logical debate, but through the use of positive and negative reinforcement.
With the behaviorist learning theory in the classroom, there are four basic types of reinforcement that can be used.
- Positive Reinforcement. This is an immediate reinforcement of a wanted behavior when it is observed. Giving a student verbal praise for a wanted behavior is a common form of positive reinforcement that teachers offer to students.
- Negative Reinforcement. Instead of offering a student a compliment, this type of reinforcement tells a student that their behavior is not wanted. The goal isn’t to embarrass the student, but to offer an alternative behavior that could bring about a desired reward.
- Presentation Punishment. This option is often used as a form of showing an entire class what will create a negative reinforcement response. If Johnny keeps yelling during story time, a teacher might bring the student up to the front of the class and then tell Johnny that his behavior is inappropriate at that moment. The goal here is to embarrass the student, but to also encourage other students not to be embarrassed by not replicating Johnny’s behavior.
- Removal Reinforcement. This may be used by removing a disruptive student with negative behaviors from the classroom. It may also be used through a period of negotiation so that a teacher gets what they want, but a student can also have something that they want.
Each reinforcement opportunity has specific benefits and disadvantages that must be considered before it is implemented in a classroom setting.
Pros and Cons of Positive Reinforcement
Pros
It offers an immediate reinforcement of a wanted behavior. Specific statements of praise help to reinforce the compliment being offered. Specific actions, such as “clipping up” or “earning a star,” can also be included to initiate rewards.
Cons
Some students aren’t motivated by rewards. They don’t care about the classroom setting and will not respond to the positive reinforcement opportunities.
Pros and Cons of Negative Reinforcement
/GettyImages-534575873-56adc8913df78cf772b7b157.jpg)
Pros
It creates an immediate “consequence” for an unwanted behavior. Some students may hear this consequence and not want to have it themselves, which will modify their behavior. It can create immediate change within a student who is motivated by rewards.
Cons
Some students are not motivated by a negative reinforcement either. “Who cares what you think?” Their behaviors are more about their individual needs and those needs don’t involve the classroom setting.
Pros and Cons of Presentation Punishment
Pros
It impacts the entire classroom. You’re able to modify the behavior of a large group by using an unwanted behavior from one individual. It can address a specific and potentially dangerous unwanted behavior immediately.
Cons
It causes the student being used as a presentation to be targeted by other students. They may make fun of that student or not want to be associated with them. Some students are sensitive and may resent being used as an example toward other students, which increases the number and the aggressiveness of their unwanted individuals.
Types Of Negative Reinforcement In The Classroom
Pros and Cons of Removal Reinforcement
Pros
It is a way to meet the needs of a specific student without disrupting the entire class. It may remove an unwanted behavior from the classroom immediately. Removal minimizes impact while allowing learning progression. It takes away something that a student sees as “good,” which encourages them to “earn it back” with wanted behaviors.
Cons
It may encourage a student to continue offering unwanted behaviors so they can get their way. They learn that there is a direct connection between behaving “badly” and getting what they want. It may cause other students in the classroom setting to behave in the same way so they can receive “special treatment” as well.
Is A Talking To Considered Negative Reinforcement
Which Option Is Right for Teachers Today?
Teachers should be using all of these options when appropriate to address wanted and unwanted behaviors in the classroom. The goal should always be to avoid an unpleasant consequence, but sometimes a punishment is necessary to remove an unwanted behavior. Teachers should never belittle a student. They should always be looking for a way to generate a positive outcome.
Examples Of Positive And Negative Reinforcement
And behaviorist learning theory in the classroom works best when an individualized approach is taken. A group consequence creates resentment in students who weren’t involved. Group rewards only reinforce unwanted behaviors in those who weren’t meeting expectations. By finding the middle ground, the classroom can really become a good learning environment.